In a world filled with uncertainties, it is crucial to have tools and techniques that can help us make informed decisions. Whether you are an engineer, economist, or researcher, understanding and representing uncertainty is essential for accurate analysis and predictions. One such powerful approach is the Monte Carlo Sampling Method, which allows us to tackle probabilistic analysis of structures. In this blog post, we will explore the necessity of earning Monte Carlo Sampling and its applications in various fields.
Embracing Uncertainty
Our understanding of various phenomena in our environment is often incomplete, leading to a degree of uncertainty. This uncertainty spans across multiple disciplines, including physics, engineering, economics, and medicine. For instance, a geologist cannot predict with certainty the behavior of soil or rock strata in an underground environment, and an economist cannot anticipate the behavior of a stock with absolute certainty. To address this challenge, it is crucial to have approaches that enable us to represent uncertainty and provide probabilistic findings.
What is Monte Carlo Analysis?
The Monte Carlo sampling method is a statistical technique utilized for estimating unknown quantities through the generation of random samples. This approach involves simulating numerous random experiments or trials and using the outcomes to approximate the desired quantity (See Figure 1). By leveraging the concepts of probability and randomness, this method offers a robust and versatile solution for addressing complex problems. By generating a diverse range of random samples, it effectively captures the inherent variability and uncertainty inherent in the problem, resulting in more accurate estimations. As the number of samples increases, the approximation becomes closer to the true value. This method finds applications in various fields, including risk analysis, optimization, machine learning, and scientific simulations. It empowers researchers and practitioners to make informed decisions based on reliable estimates and statistical measures.
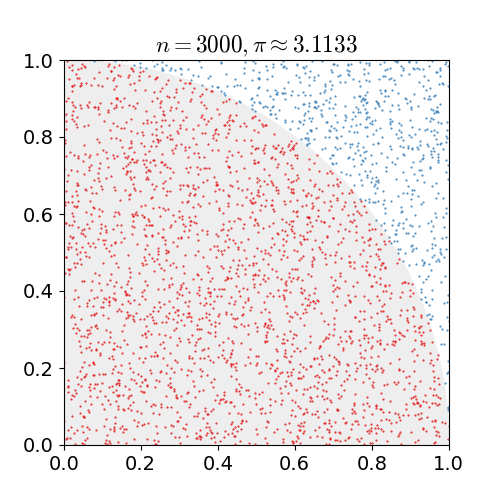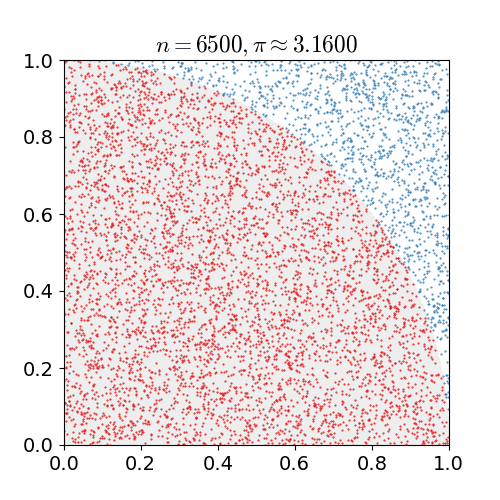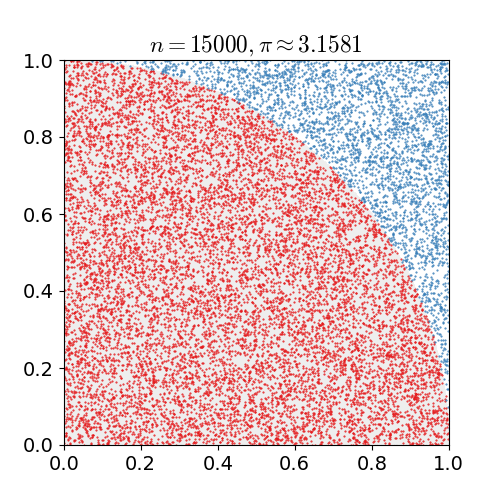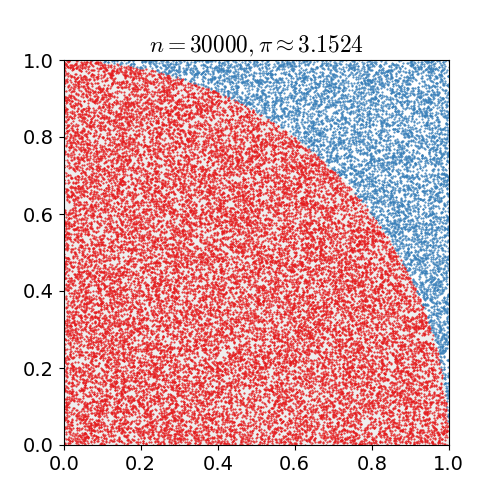
Figure 1 Monte Carlo method to estimate π value
The Necessity of Monte Carlo Sampling
Monte Carlo Sampling is a powerful technique that allows us to simulate and analyze complex systems with uncertain parameters. By generating a large number of random samples, we can obtain statistical distributions and make probabilistic predictions. This method is particularly useful when traditional analytical methods fail due to the complexity of the problem or the lack of complete information. Monte Carlo Sampling provides a way to account for uncertainties and make informed decisions based on probabilistic analysis.
Introducing the Online Course
Are you interested in mastering the Monte Carlo Sampling Method for probabilistic analysis of structures? Look no further! Our online course offers a comprehensive understanding of this powerful technique, even for non-experts in statistics and probability.
What will you learn in this course?
- Understand the fundamentals of uncertainty modeling and its importance in various fields.
- Explore the Monte Carlo Sampling Method and its applications in probabilistic analysis of structures.
- Learn how to generate random samples and analyze statistical distributions.
- Gain practical skills to apply Monte Carlo Sampling in real-world scenarios.
- Enhance your decision-making abilities by incorporating probabilistic analysis into your work.
Who can benefit from this course?
- Engineers seeking to improve their understanding of uncertainty in structural analysis.
- Economists looking to incorporate probabilistic modeling into their stock market predictions.
- Researchers in various fields who want to make more accurate predictions by accounting for uncertainties.
- Students and professionals interested in expanding their knowledge of statistics and probability.
Don’t miss this opportunity to enhance your skills and make more informed decisions in your field. Enroll in our Monte Carlo Sampling course today and embark on a journey to master the Monte Carlo Sampling Method for probabilistic analysis of structures.
